Malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases
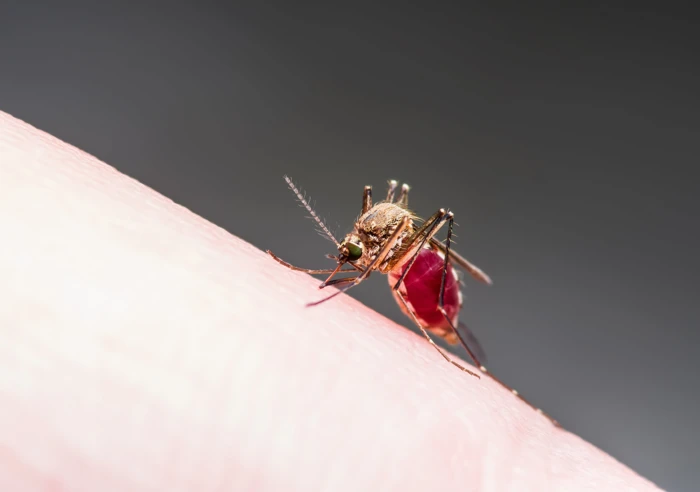
Mosquitos are the most lethal animal species to humans. Annually, diseases transmitted by mosquitoes kill more than one million people and infect up to 700 million. These diseases include malaria, dengue, Zika and Japanese encephalitis. Malaria causes over half of these deaths. Now, climate change is driving mosquitos into areas previously unaffected. In Europe, over the past decade, locally transmitted dengue outbreaks have increased. Burnet collaborates with teams worldwide to reduce the burden of mosquito-borne diseases and protect people at risk.
Malaria challenges
Malaria is the deadliest mosquito-borne disease. In 2023, there were an estimated 263 million malaria cases and 597,000 deaths in 83 countries. That amounts to approximately 68 deaths per hour. Ninety-five per cent of malaria-related deaths were in Africa. Seventy-six of these deaths were children under 5.
Malaria is caused when female Anopheles mosquitoes spread the Plasmodium parasite between humans.
The most significant Plasmodium species are:
- P. falciparum, which causes the most deaths and is most common in Africa
- P. vivax, which kills fewer people but can recur after lying dormant in the liver; harder to detect, it’s the most common species in the Pacific and Southeast Asia.
After decades of public health effort, malaria was officially eliminated from Australia in 1981. However, reintroduction remains a risk.
Malaria is endemic in approximately 85 countries, including the Americas, Africa, Southeast Asia, Western Pacific and the Eastern Mediterranean region.
Malaria challenges include:
- mosquitos becoming resistant to insecticides
- parasites becoming resistant to anti-malarial drugs
- warmer temperatures expanding mosquito habitats, spreading malaria to non-tropical regions
- malaria-control programs losing funds due to lack of political will to continue them
- health systems in low-resource areas providing limited care to vulnerable populations
- limited effectiveness of current vaccines, lack of a vaccine for P. vivax
- lack of an endorsed malaria vaccine for the Asia-Pacific region
- rapid diagnostic tests becoming ineffective.
There's also a lack of sensitive tools for:
- detecting and tracking the diversity of Plasmodium and Anopheles species
- diagnosing low density or asymptomatic infections
- detecting dormant liver-stage infections by Plasmodium.
Stories
View 28 more
Australia's frontline defence against chikungunya
While the outbreak of the mosquito-borne chikungunya virus in China raises the prospect of more widespread transmission, scientific research has provided Australia with a special biological line of defence.

Burnet researcher developing first human organoid structure to study malaria
Dr Mayimuna Nalubega’s work is hoped to accelerate progress toward more effective vaccines and transform how scientists understand malaria immunity.

Mapping malaria risks
Other mosquito-borne diseases
We research other diseases carried by mosquitoes, including:
- dengue: the most widespread mosquito-borne viral disease, increasingly common in the Pacific and parts of northern Australia
- Zika virus and Japanese encephalitis: emerging threats with pandemic potential; Japanese Encephalitis might be endemic in Australia
- Ross River virus and Barmah Forest virus: already endemic in Australia
- chikungunya: it can cause similar symptoms to Zika and dengue; a compatible mosquito carrier already exists in Australia.
Climate change and mosquito-borne diseases
Climate change enables mosquitoes and the diseases they carry to spread into new regions. If health systems in such regions have limited resources, mosquito-borne diseases could become established there.
Our expertise
We combine laboratory discovery with public health implementation and expertise in international development.
We also work in close partnership with communities and health systems across Africa, Southeast Asia and the Pacific.
Global objectives
Our work aligns with the World Health Organization’s Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030, including:
- a reduction of malaria case incidence and mortality rates by at least 90%
- malaria eliminated in at least 35 countries
- preventing re-establishment in malaria-free countries
- the transformation of malaria surveillance into a core intervention
- fostering innovation and expanding access to tools and technologies.
Diagnostics and surveillance
We develop and evaluate new diagnostic technologies to support earlier, more accurate detection of malaria, dengue, Zika and Japanese encephalitis. This includes tools for improved case management, genomic surveillance and resistance monitoring. For example, we’re investigating the integration of more sensitive malaria detection techniques into national surveillance systems.
Immunity and vaccines
We focus on understanding immune responses to Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax to inform effective vaccine design.
Our laboratory research advances the development and evaluation of leading malaria vaccine candidates. For example, we’re researching immune responses generated by malaria vaccination in young children across Africa.
Drug discovery and resistance
We are developing new antimalarial drugs and tracking and preventing the spread of drug resistance, especially in the Asia-Pacific region.
We aim to accelerate deployment of new treatments. For example, we are researching new antimalarial drugs to overcome Plasmodium drug resistance.
Epidemiology and public health
Burnet conducts implementation research to improve healthcare services and malaria prevention.
We support modelling and evaluation of interventions for malaria across endemic regions. For example, in the Indo-Pacific region, our ADVANCE project aims to improve access to new malaria diagnostic tools.
Mosquito control
To achieve malaria elimination goals, we research mosquito behaviour and integrated control strategies.
To control the spread of viruses such as dengue, Zika and chikungunya, we study and evaluate use of the Wolbachia bacterium.
Our achievements
Burnet is at the forefront of research into mosquito-borne diseases. Our work influences global health policies, clinical guidelines and vaccine development.
Surveillance systems
In Papua New Guinea and the Greater Mekong region, we demonstrated how community-led molecular and serological surveillance can be integrated into national systems.
Digital innovation
In the Greater Mekong region and Papua New Guinea, we developed mobile app-based advanced malaria surveillance tools to improve case detection, surveillance and use of data for informed decision-making.
Vaccine design
We study targets from malaria parasites around the world. By knowing how much they differ, we can create a ‘guide’ to develop vaccines that work in multiple regions and against different strains.
We also delivered critical insights into the performance of the RTS,S malaria vaccine among young children in a malaria-endemic area.
Vaccine development
We identified protective antibody targets and predicted antigen combinations for highly effective vaccines. This work directly informed international vaccine development.
Drug resistance
In Papua New Guinea, we discovered a local emergence of artemisinin resistance mutations. This led to the World Health Organization (WHO) changing its definition of artemisinin resistance, increasing the accuracy of resistance surveillance.
Vector control
Burnet led the first trial demonstrating how personal mosquito repellent can prevent malaria. The WHO used this evidence to inform their regional policy. Together with partners in PNG, we are evaluating new vector control tools to target outdoor transmission.
Maternal and newborn health
We provided the first evidence that artemisinin drugs are safe to use in early pregnancy. As a result, the WHO revised its treatment guidelines. Our research linked malaria to 200,000 global stillbirths per year and showed how preventive treatment reduces the risk. Informed by our work, the WHO updated its policy in Asia.
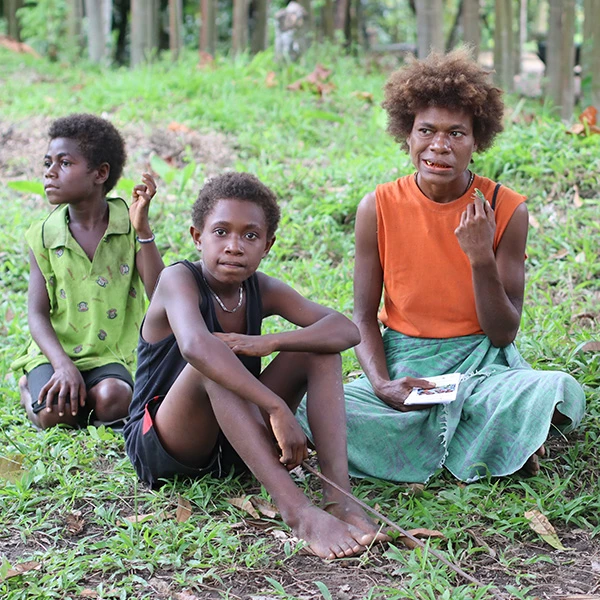

Partnering to eliminate malaria in our region
Burnet, WEHI and the Australian Government have teamed up to work on malaria elimination with countries across the Pacific and South-East Asia.
Featured publications
Sulfonylpiperazine compounds prevent Plasmodium falciparum invasion of red blood cells through interference with actin-1/profilin dynamics
PLoS Biology
Madeline G. Dans et al
Aryl amino acetamides prevent Plasmodium falciparum ring development via targeting the lipid-transfer protein PfSTART1
Nature Communications
Madeline G. Dans et al
Single cell transcriptomics shows that malaria promotes unique regulatory responses across multiple immune cell subsets
Nature Communications
Julianne Hamelink
Antibody mechanisms of protection against malaria in RTS,S-vaccinated children: a post-hoc serological analysis of phase 2 trial
The Lancet Microbe
Liriye Kurtovic et al
Our projects
View 40 more
Discovering novel antimalarials to block parasite invasion of human cells
Drugs are the main weapons used to combat malaria infection. However, parasites are becoming resistant and new medicines and drug targets are needed.
Understanding immunity mediated by the RTS,S malaria vaccine in children
We're researching the immune responses induced by the RTS,S vaccine where the burden of malaria is highest: among young children in multiple malaria-endemic African countries.

Germinal centre organoids to investigate human immune response to infection and vaccination
We're using germinal centre organoid models to investigate human immune development to malaria parasites and malaria vaccines.
Our working groups

























